
相信每位家長都想給孩子最好的照顧。但當孩子生病時, 尤其新手爸媽都會像考試般如臨大敵。剛經歷過新冠疫情,轉眼又到流感高峰,連普通傷風感冒都彷彿變得更頻密,令不少爸媽感嘆小朋友病完又病。在此提提大家,如果醫生處方了抗生素,記住要同時保護腸道好菌!
其實當小朋友卸下口罩等防疫裝備,重新接觸周邊環境,自然增加了接觸外來病菌的機會。若小朋友免疫系統未夠完善,便會較易病倒。在康復過程中,身體會產生抗體,抵抗力便會比原來的更強。小朋友成長期間,通過反覆的生病和康復,他們的免疫系統會漸漸建立起來,家長無需過份擔心。
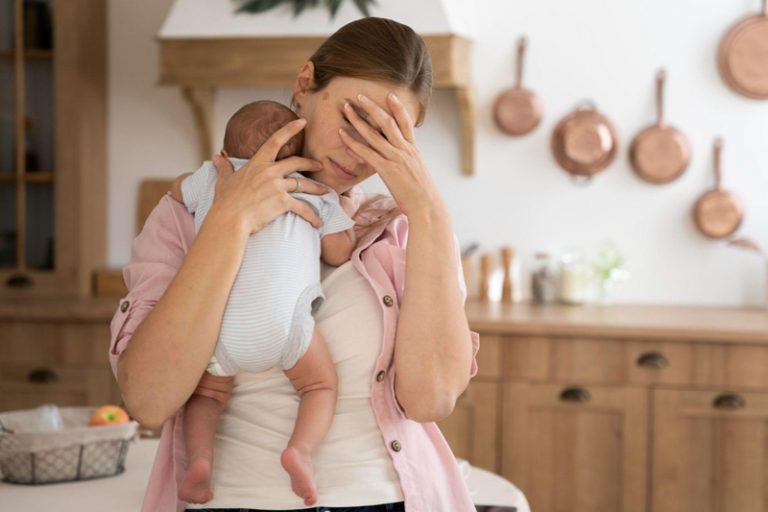

康復後,雖然免疫力普遍會隨時間增強,但嬰幼兒的腸道好菌被破壞後,卻未必能完全恢復至病前的平衡狀態。不舒服、腹瀉、胃口差而令整個人仔都好像小了一個碼。註冊藥劑師葉榮煒表示:「大家可能有聽過新冠會導致菌群失衡,但其實流感,甚至普通傷風感冒也會擾亂腸道微生態1。三歲前,嬰幼兒腸道菌群很容易受到環境因素的影響。而三歲後,腸道菌種的構成則已經成形,是好是壞日後也較難改變。」因此,三歲前的嬰幼兒需要加倍照顧,保護腸道好菌,讓菌群更加豐富和多樣化。
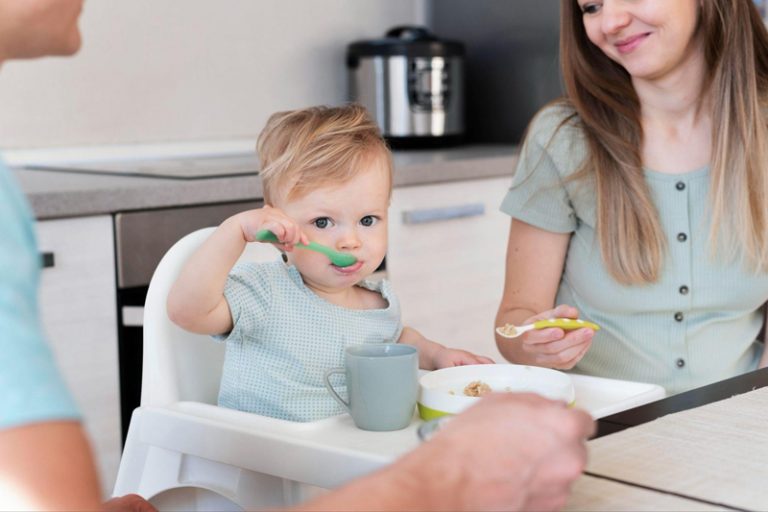

不論男女老幼,抗生素是十分常見的醫生處方藥。雖然抗生素的目的是殺滅致病細菌,但好菌也難免受牽連。葉榮煒提醒:「抗生素是一把雙刃刀。經醫生診斷處方並適當使用,抗生素是很有效的藥物治療,能幫助擊退致病細菌,減輕病情和加快康復。同時抗生素亦會無可避免地減少腸道好菌,令菌群失衡。」
研究證實,服用抗生素會大大減少腸道中乳酸桿菌及雙歧桿菌等好菌的數量,亦可能因而影響腸胃消化、免疫系統及呼吸道健康2,3。另外,一項12,422名兒童參與的研究顯示,在嬰兒期曾使用抗生素的兒童,對成長也有一定影響4。
葉榮煒建議給患傷風感冒的小朋友保護好腸道菌群。如需服食抗生素,除了一般日常保健的活性益生菌外,更應考慮選擇穩定性及效能更高的滅活菌(或稱後生元)。大家較熟悉的活性益生菌,普遍在抗生素治療下都可能受到影響,因而失去功效。如有其他憂慮或不明白的地方,也可向醫生或藥劑師查詢。
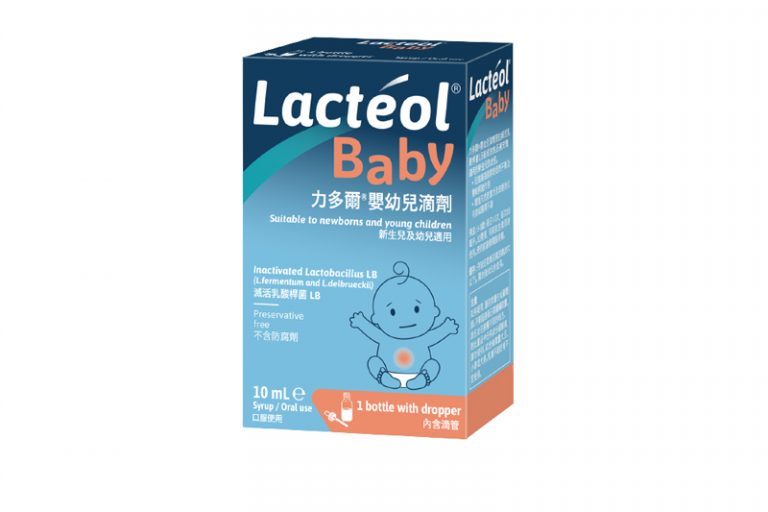

*滅活LB菌=滅活乳酸桿菌LB(inactivated Lactobacillus LB)
參考資料:
延伸閱讀

